Effective Ways to Balance Hormones Naturally and Improve Well-Being
The hormone most commonly associated with depression is serotonin, a neurotransmitter rather than a hormone in the traditional sense, which plays a crucial role in mood regulation, sleep, and emotional well-being. A deficiency or imbalance in serotonin levels is often linked to depression.
Balancing hormones naturally or with medical intervention requires a combination of lifestyle adjustments, dietary changes, stress management, and sometimes medication. Below are ways to address hormone imbalances, including those linked to depression:
1. Support Serotonin Production
- Dietary Adjustments: Consume foods rich in tryptophan (eggs, dairy, nuts, seeds, fish) as it helps in serotonin synthesis.
- Exercise: Regular aerobic activities like walking, running, or yoga can boost serotonin.
- Sunlight Exposure: Spend 15-30 minutes outdoors daily or use light therapy during darker months.
- Gut Health: Include probiotics (yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut) to support serotonin production in the gut.
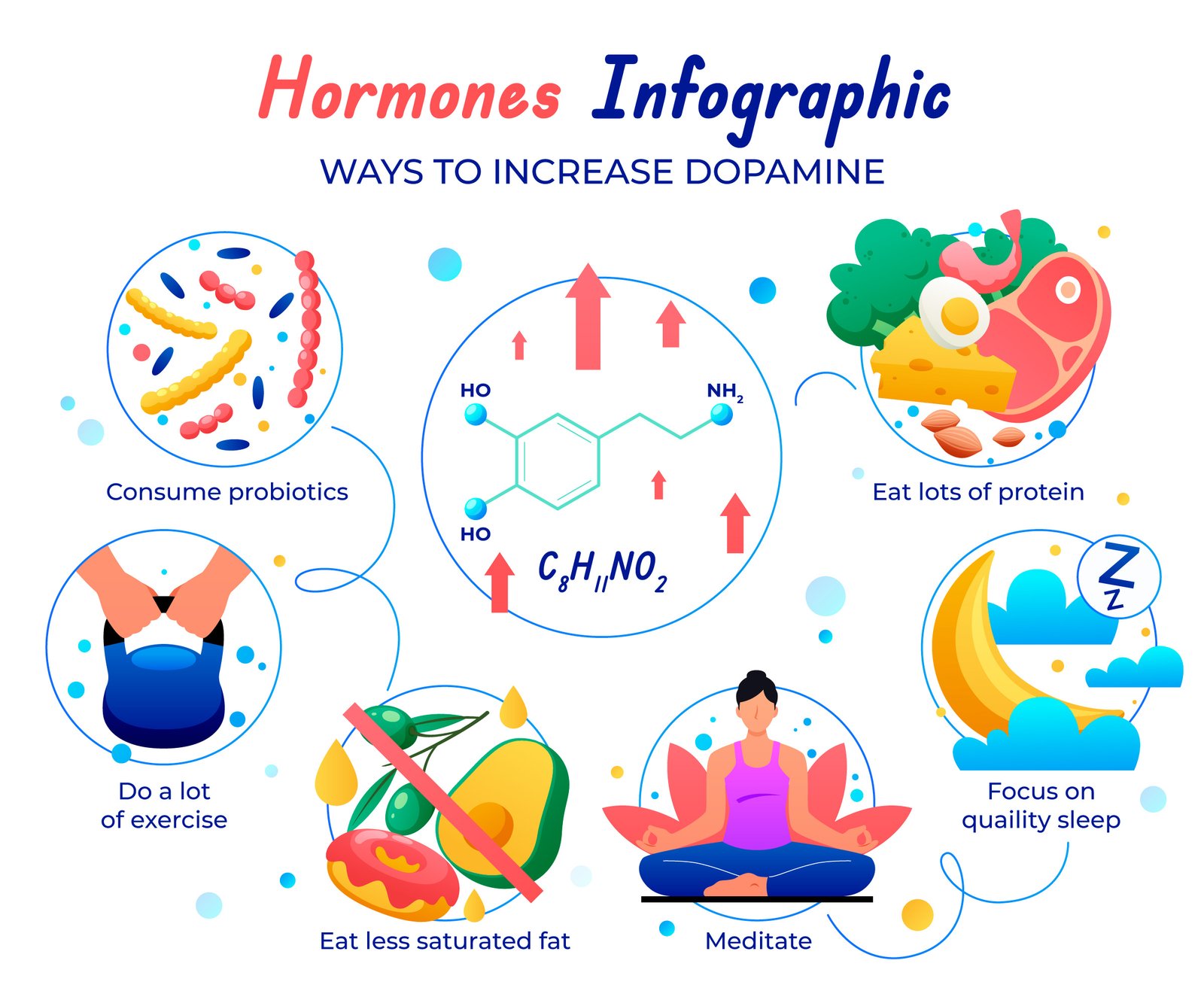
2. Boost Dopamine Levels
- Protein-Rich Foods: Chicken, fish, beans, and lentils contain amino acids that aid dopamine synthesis.
- Supplements: L-tyrosine, an amino acid, may help.
- Rewarding Activities: Engage in hobbies or tasks that bring joy to activate dopamine pathways.
3. Balance Norepinephrine
- Mindfulness Practices: Meditation and deep breathing lower stress, reducing norepinephrine imbalances.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Found in fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts, these support brain function and norepinephrine levels.
4. Lower Cortisol
- Stress Reduction:
- Practice relaxation techniques like meditation, tai chi, or journaling.
- Get quality sleep; aim for 7-9 hours nightly.
- Dietary Changes:
- Limit caffeine and sugar intake.
- Add anti-inflammatory foods like berries, turmeric, and leafy greens.
- Adaptogens: Herbs like ashwagandha, rhodiola, and holy basil help regulate cortisol.
5. Optimize Oxytocin
- Positive Social Interactions: Spend time with loved ones or engage in meaningful relationships.
- Physical Touch: Hugs, massages, and even petting animals can increase oxytocin.
- Mindful Acts: Volunteering or acts of kindness boost oxytocin.
6. Support Thyroid Health
- Nutritional Support:
- Ensure adequate iodine intake (seaweed, iodized salt).
- Selenium-rich foods (Brazil nuts, sunflower seeds) support thyroid function.
- Zinc and iron (meat, shellfish, legumes) are essential for hormone production.
- Avoid Toxins: Reduce exposure to endocrine disruptors in plastics and processed foods.
- Medical Support: Consult a doctor for thyroid hormone replacement therapy if needed.
7. Regulate Estrogen and Progesterone
- Balance Diet:
- Cruciferous vegetables (broccoli, kale) help metabolize estrogen.
- Healthy fats (avocado, olive oil) support hormone synthesis.
- Lifestyle:
- Regular exercise helps stabilize hormonal fluctuations.
- Avoid alcohol and processed foods.
- Herbal Remedies:
- Chasteberry (vitex) can help balance progesterone.
- Black cohosh is often used for estrogen-related symptoms.
8. General Tips for Hormonal Balance
- Maintain a Balanced Diet:
- Focus on whole, nutrient-dense foods.
- Avoid excessive refined carbs and sugars.
- Stay Active:
- Incorporate strength training, yoga, or swimming to promote hormonal health.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water to support overall body function.
- Quality Sleep:
- Establish a regular sleep schedule.
- Reduce screen time before bed.
- Reduce Inflammation:
- Incorporate anti-inflammatory foods like turmeric, ginger, and omega-3-rich fish.
- Avoid Endocrine Disruptors:
- Use natural skincare and household products.
- Avoid plastics and processed foods with chemical additives.
9. Supplements to Consider
- Magnesium: Helps regulate stress hormones.
- Vitamin D: Critical for serotonin production.
- B Vitamins: Essential for energy and hormone synthesis.
- Probiotics: Support gut health, indirectly improving hormonal balance.
- Herbal Adaptogens: Ashwagandha, rhodiola, and ginseng can stabilize cortisol and improve resilience to stress.
10. Medical Interventions
If natural remedies are insufficient, consult a healthcare provider for potential treatments:
- Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT): For conditions like hypothyroidism or menopause.
- Medications: SSRIs for serotonin, thyroid medications for thyroid imbalances, or specific supplements for deficiencies.
- Regular Monitoring: Get blood tests to check hormone levels and adjust treatments accordingly.
By adopting these strategies and seeking medical advice when necessary, you can effectively address hormone imbalances and improve overall health and well-being.